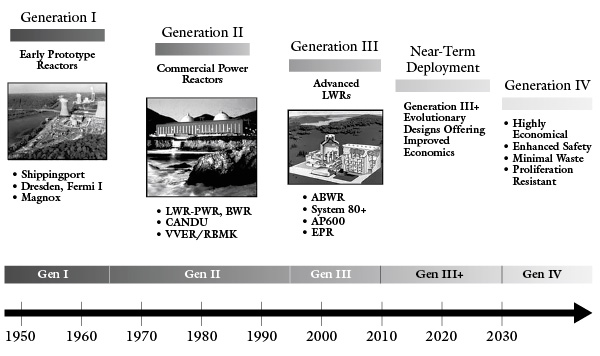
Nuclear power is one of the most important scientific and technological developments of the 20th century. Its history begins with scientific discoveries in the 19th century and evolves into a technology that has changed the way the world produces energy. In this article, we will explore how nuclear power has evolved from its discovery to modern nuclear power plants.
The First Discoveries
- Radioactivity (1896): Henri Becquerel discovered radioactivity by accident, when he observed that uranium salts emitted radiation without any external energy source.
- Marie and Pierre Curie: The Curie pair isolated the radioactive elements polonium and radium, expanding our understanding of radioactivity.
- The Model of the Atom: In the early 20th century, Ernest Rutherford and later Niels Bohr developed models that explained the structure of the atom and the role of the nucleus.
The Discovery of Nuclear Fission
A major advance in understanding nuclear energy came in 1938, when German scientists Otto Hahn and Fritz Strassmann discovered nuclear fission. In fission, the uranium nucleus splits into smaller pieces, releasing enormous amounts of energy. This work was further developed by Lise Meitner and Otto Frisch, who explained the physics behind the phenomenon.
The Manhattan Project Era
During World War II, scientific discoveries about nuclear energy were used to create the first atomic bomb. The Manhattan Project (1942–1945) in the United States brought together scientists from around the world to build nuclear weapons. This project led to the first nuclear tests and the use of nuclear weapons in Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
The Peaceful Use of Nuclear Energy
After the war, scientists and governments began to look into the peaceful uses of nuclear energy. Some of the important milestones include:
- The First Nuclear Power Plant (1954): The first nuclear power plant was built in Obninsk, Soviet Union.
- Spread of Nuclear Energy (1960-1980): During these decades, many stations were built around the world, with the United States, Europe, and Japan leading the way.
Major Accidents and Impacts
The history of nuclear energy includes serious accidents that highlighted the dangers of this technology:
- Three Mile Island (1979): A partial core meltdown occurred in one of the reactors at the Three Mile Island nuclear power plant in Pennsylvania, United States. Although there was no significant release of radioactivity into the environment, the event shook public confidence and led to stricter regulations on nuclear safety.
- Chernobyl (1986): The disaster at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant in Ukraine had enormous health and environmental consequences, affecting millions of people.
- Fukushima (2011): An earthquake and tsunami caused severe damage to the Fukushima nuclear power plant in Japan, leading to a core meltdown and radioactive leaks.
Nuclear Energy Today
Despite the risks, nuclear power remains an important source of energy in many countries. The main features of today's nuclear technology include:
- Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): New, safer and more flexible reactors gaining ground.
- Nuclear Fusion Research: Although still in an experimental stage, fusion promises cleaner and unlimited energy in the future.
The history of nuclear energy is full of innovations, challenges and lessons. From the first discoveries in the 19th century to modern nuclear power plants, nuclear energy remains at the center of scientific research and energy policy, aiming to contribute to a more sustainable world.