Chernobyl nuclear accident
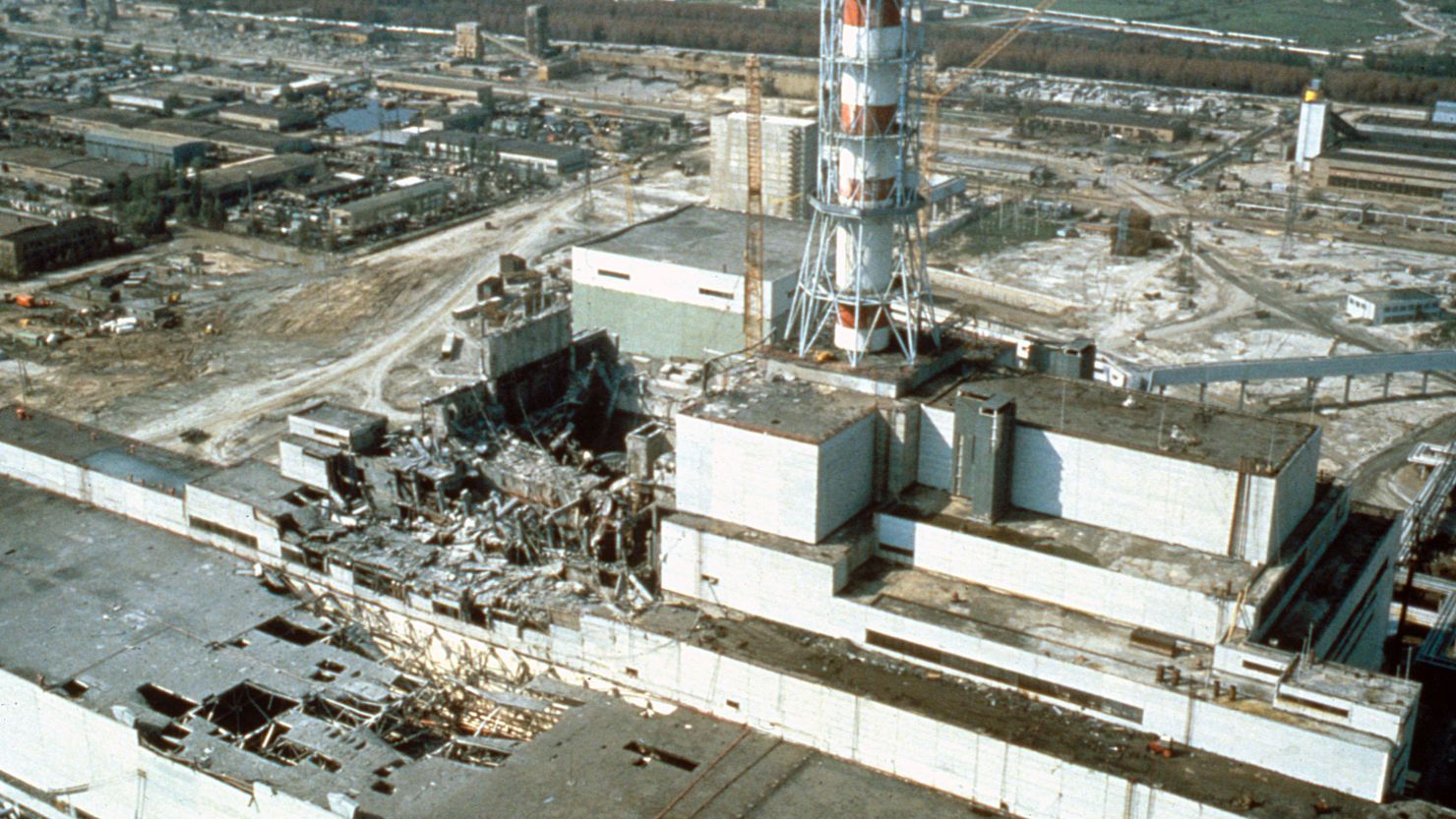
At April 26, 1986, the worst nuclear accident in human history occurred. Reactor 4 of the nuclear power plant in Chernobyl (Chernobyl) in the then Soviet Union (now Ukraine) exploded during a test experiment. The accident had devastating consequences for the environment, human health and the international nuclear industry.
What happened
The disaster began during a safety experiment that was intended to test how the reactor would operate in the event of a power outage. Due to design flaws in the reactor type RBMK and operator errors, the situation got out of control.
- Sudden Power Increase: The reactor's power increased explosively.
- Explosion: The heat caused the core to explode and release huge amounts of radioactivity into the atmosphere.
- Fire: The flames that broke out made it even more difficult to control the situation, while scattering radioactive particles over a wide radius.
The Effects
Radioactive Pollution
- The accident liberated 400 times more radioactive than the Hiroshima bomb.
- Radioactive elements such as iodine-131, the cesium-137 and the Strontium-90 they still pollute the environment around the area.
Human Lives
- First deaths: 2 workers died immediately from the explosion, while dozens of others died in the following days from acute radioactive disease.
- Chronic effects: Thousands of people suffered from thyroid cancer and other diseases linked to radiation exposure.
Area Evacuation
- About 350,000 people were forced to abandon their homes.
- The city Pripyat, which was located near the station, was abandoned and remains a ghost town to this day.
Dealing with the Accident
- Cleaning Company: Approximately 600,000 people, known as “liquefiers”, participated in the cleanup of the area, exposed to high levels of radioactivity.
- Construction of a Sarcophagus: A huge concrete enclosure was built around the damaged reactor to contain the leakage of radioactivity.
In 2016, a new metal casing was constructed, known as “New Safe Confinement”, which will protect the area for the next 100 years.
The International Consequences
Chernobyl dramatically affected the international community:
- Led to stricter regulations for the safety of nuclear power plants.
- Caused decline in public acceptance for the use of nuclear energy, especially in Europe.
- It strengthened cooperation between states in managing nuclear emergencies.
The Legacy of Chernobyl
Today, Chernobyl remains a living monument to the devastating consequences of nuclear power when proper safety standards are not followed. The area around the station has been transformed into exclusion zone, which remains dangerous, but at the same time hosts nature that was reborn without the presence of humans.
Conclusion
Chernobyl is a story of destruction, sacrifice, and a reassessment of our technological choices. This tragedy reminds us that safety must always be at the heart of all technological progress.