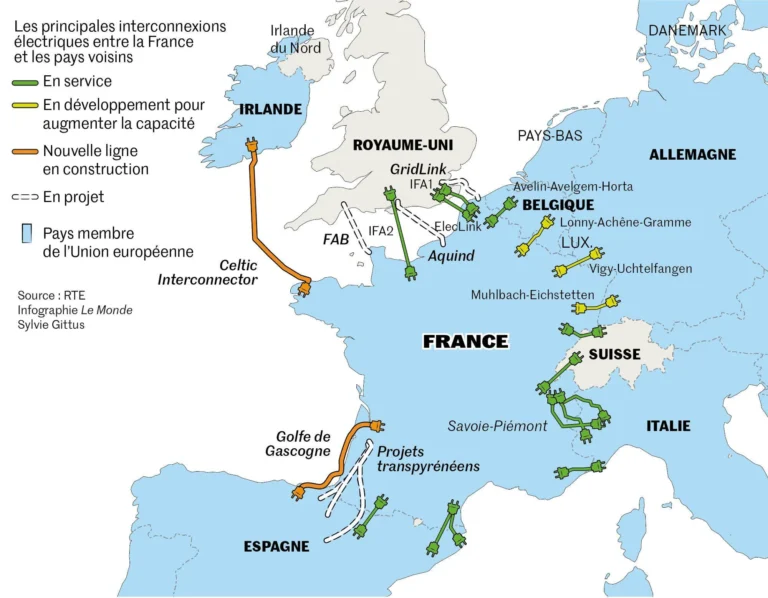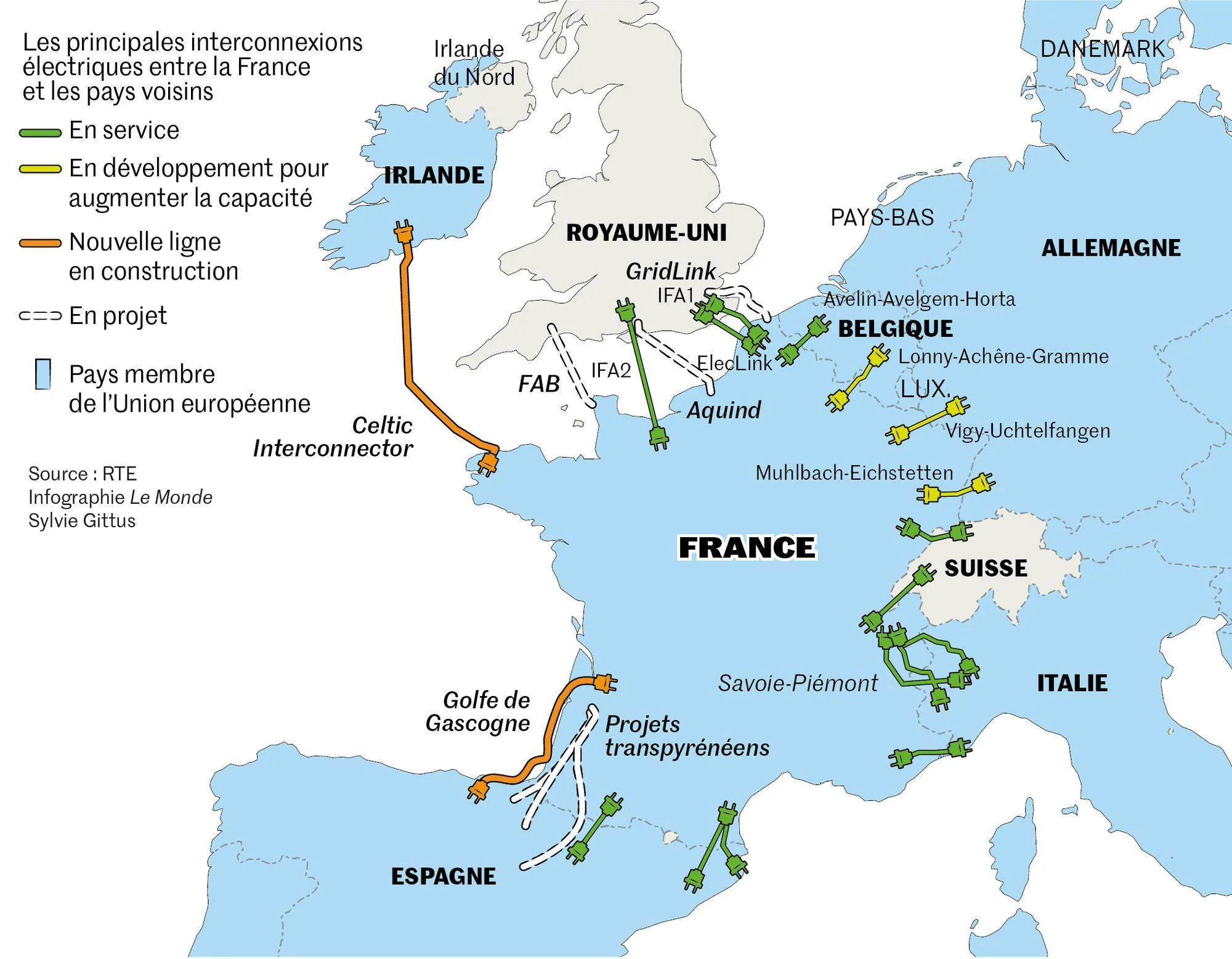
Image source: https://www.reddit.com/r/europe/comments/18v174k/international_electricity_interconnections_key_to/
The interconnection of electricity networks between nuclear and non-nuclear countries is a cornerstone for energy security and sustainability in Europe and globally. These interconnections allow the exchange of electricity, balancing demand and supply, and enhancing the reliability of energy systems.
The importance of electrical interconnection becomes even more evident in times of increased demand or emergencies, where countries without nuclear generation can import energy from neighboring countries with stable nuclear generation. At the same time, interconnection facilitates the integration of renewable sources and reduces the cost of electricity.
Interconnection technologies
The main technologies used to interconnect electrical networks include:
- Alternating Current (AC): It is used to connect neighboring countries with similar grid frequencies. AC technologies are suitable for short to medium distances and are cheaper to implement than HVDC.
- High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC): It allows the connection of remote areas and the interconnection of systems with different frequencies or technical specifications. HVDC technology is ideal for long distances or underwater connections, as it reduces energy losses.
Example: The interconnection between Poland and Lithuania via the LitPol Link uses HVDC technology to enhance grid stability and security of supply. (Next Power Plants)
Benefits of connections
- Supply Security: Interconnection allows for the exchange of energy during periods of high demand or emergencies.Example: In the winter of 2021, Germany faced high electricity demand due to a cold snap. Additional energy was imported through interconnections with France, which has nuclear power generation, to meet demand and avoid power outages. (ENTSO-E report 2021)
- Utilization of Renewable Resources: The integration of renewable energy sources from countries without nuclear power can be enhanced through interconnections.Example: Denmark generates much of its energy from wind turbines. When production is high and domestic demand is low, the surplus is exported through interconnections to countries such as Germany and Sweden, fully utilizing the clean energy produced. (Energinet.dk)
- Economic Benefits: Energy exchange can reduce the cost of electricity production and consumption.Example: Italy imports cheaper nuclear power from France during peak hours, reducing the need to turn on expensive gas-fired plants. This leads to a reduction in the price of electricity for consumers. (Terna.it)
Challenges and limitations
- Political Differences: Different energy policies between countries may affect interconnections, especially in matters of supporting nuclear or renewable energy.
- Technical Specifications: Differences in the technical specifications of the networks may require additional investments in transformers, HVDC systems and energy management software.
- Geopolitical Factors: Strategic and geopolitical decisions may affect cooperation between countries and delay or limit the expansion of interconnections.
Conclusions
Cooperation between countries with and without nuclear power through electricity grid interconnections is crucial to achieving energy security and sustainability. Technological progress, investments in HVDC systems and political will are necessary to overcome the challenges and strengthen cooperation.
Interconnections contribute to cost savings, better utilization of renewable sources and reduction of risks of electricity shortages, making the European and global energy map more stable and sustainable.