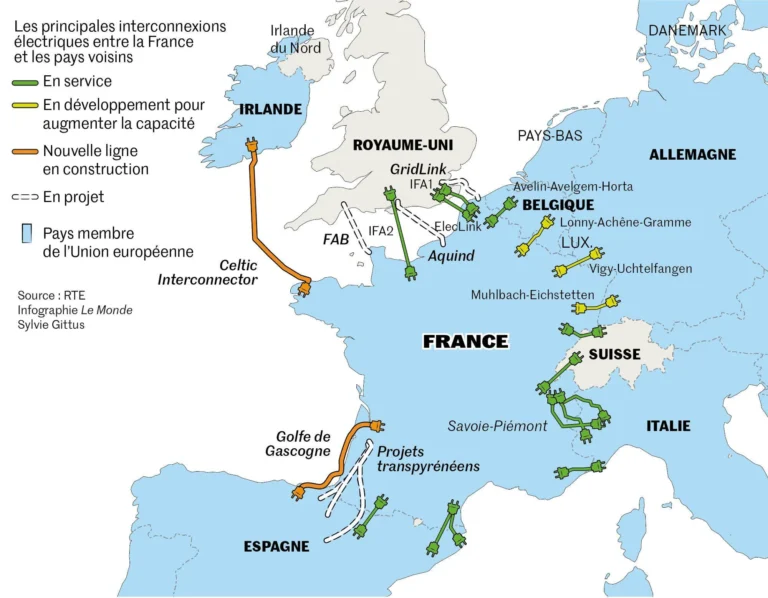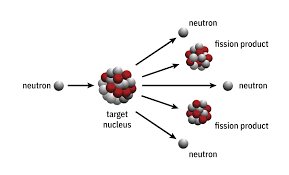
nuclear fission
OR nuclear fission is a process in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two smaller nuclei, releasing enormous amounts of energy. This process is the basis for the operation of nuclear reactors and the production of energy in nuclear power plants.
How Does Nuclear Fission Happen?
Fission occurs when a heavy nucleus, such as uranium-235 or plutonium-239, is bombarded with neutrons. The result is that the neutron is absorbed by the nucleus, which becomes unstable and eventually breaks into two or more fission products, such as barium and krypton.
During the split:
- Neutrons are released: These can cause new fissions, creating a chain reaction.
- Energy is produced: In the form of heat and radiation.
Applications of Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission has many practical applications, such as:
- Electricity Generation: Nuclear reactors use the energy produced by fission to heat water and drive turbines.
- Medicine: It is used to produce radioisotopes, which help in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases.
- Arms: Fission is the basis for the construction of nuclear weapons, although their use is strictly controlled.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages:
- It produces huge amounts of energy from a small amount of fuel.
- It does not emit carbon dioxide, contributing to the reduction of climate change.
Disadvantages:
- It creates radioactive waste that requires special management.
- There is a risk of accidents, like those at Chernobyl and Fukushima.
The Future of Nuclear Fission
Nuclear fission remains an important way to produce energy. However, research is focused on improving reactor safety and reducing radioactive waste. At the same time, nuclear fusion, which is considered safer and cleaner, may replace fission in the future.
Conclusion
Nuclear fission is a highly efficient energy-producing process, with significant challenges and opportunities. By better understanding the science behind it, we can reap its benefits while limiting its negative impacts.